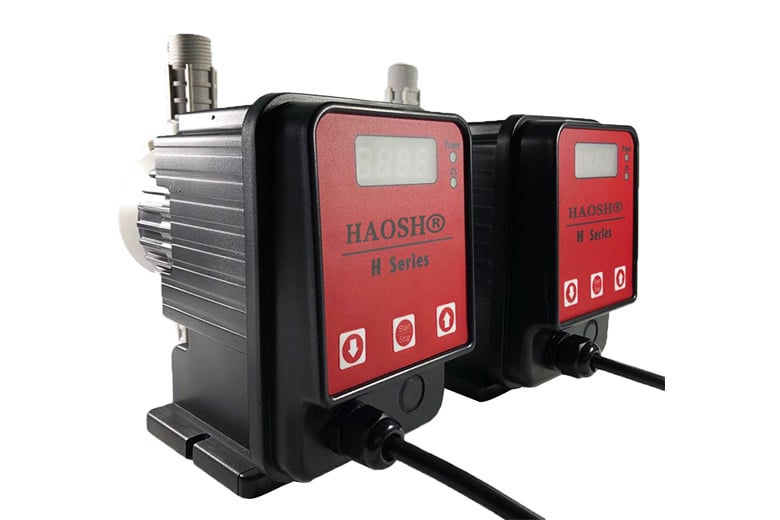
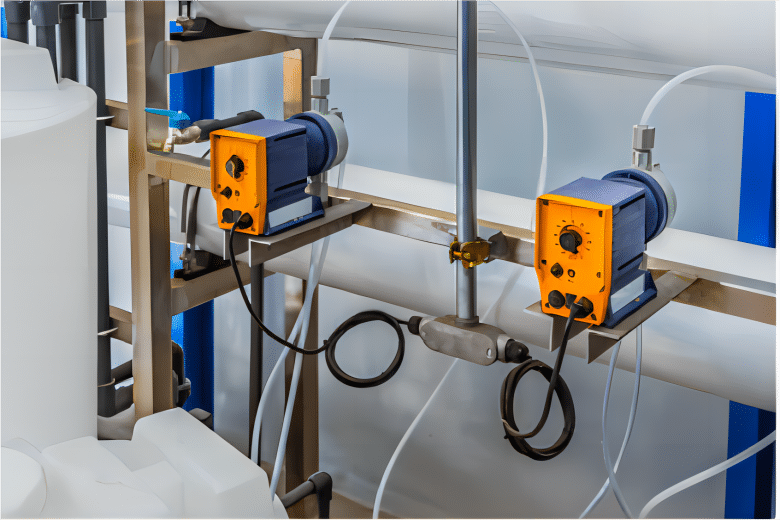
Solenoid Dosing Pump
HAOSH electromagnetic driven metering pumps are available in flow rates from 0.4 to 80 L/H and back pressures from 16 to 1.5 bar. To be able to meter almost any liquid chemical, HAOSH uses a very wide range of materials to help customers’ various applications run smoothly.
The solenoid pump has almost no wear on the drive because there is only one moving part. The pump does not require lubricated bearings or shafts, so maintenance and repair costs are very low. The continuous operation characteristics are very good.
how does a solenoid pump work?
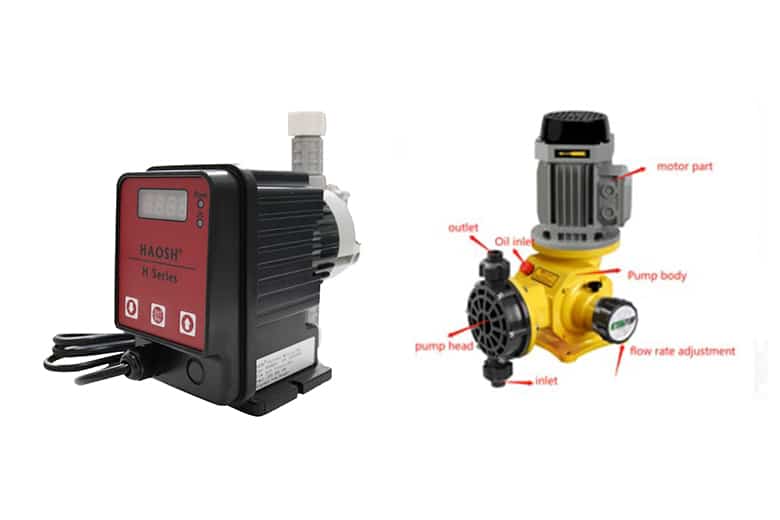
Solenoid driven dosing pumps have two main components, the actuator and the hydraulic end. The actuator uses an electronic pulse unit (EPU) to energize the solenoid coil. The solenoid then moves the solenoid shaft forward and backward by opening and closing. This stroke motion is transferred to the diaphragm in the metering head. Two check valves prevent the feed chemical from flowing back during pumping. The stroke length and stroke rate can be adjusted precisely to vary the dosing rate of the HAOSH solenoid-driven metering pump.
Industry applications
Solenoid dosing pumps are particularly suitable for applications that convey small flows of low pressure line liquids.
- Drinking water treatment: disinfectants
- Wastewater treatment: flocculants
- Cooling water: corrosion inhibitors and biocides
- Paper industry: additives