What Is Dosing Metering Pump & How It Works?
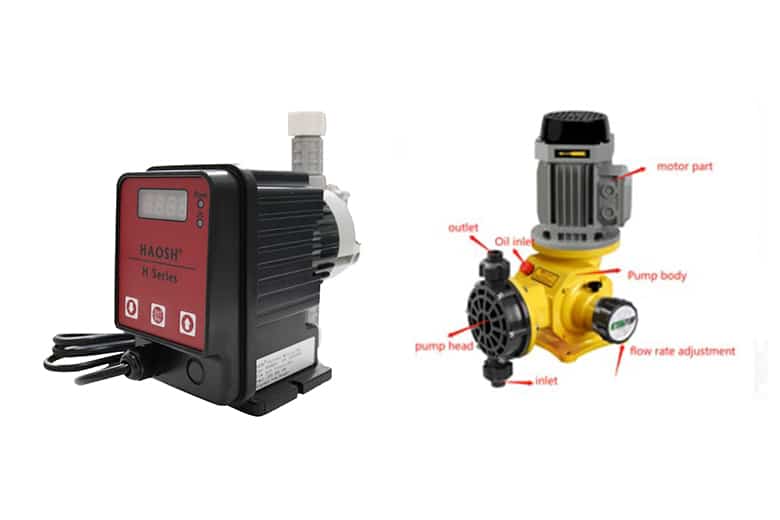

What is a dosing metering pump?
A dosing metering pump is a positive displacement pump used to inject chemical liquids into a water or gas stream at a precise flow rate. It is called by many names, such as dosing pump, metering pump, proportional pump and quantitative pump. Dosing pumps are also a central part of an integrated dosing system for automation science. They are pumps designed to dispense specific amounts of fluid and measure flow control, using expansion and contraction chambers to move the fluid. Pumped fluids include acids and bases, slurries and viscous liquids.
How does the dosing metering pump work?
Metering pump draws a certain amount of liquid into its chamber and injects the chemical liquid into the tank or pipe containing the fluid being metered. The drive power comes from an electric motor or pneumatic actuator, and there is a controller that turns the pump on and off and manages the flow rate.
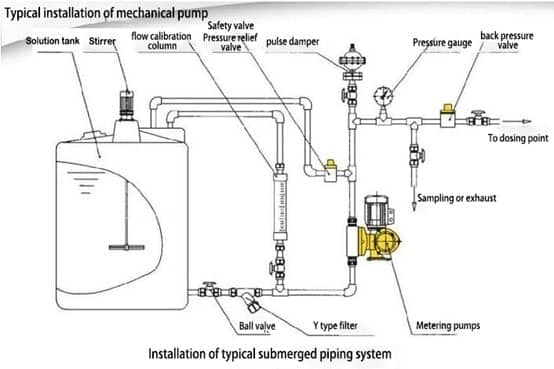
Therefore, the working principle can also be divided into motor-driven metering pumps and electromagnetic-driven metering pumps according to the power source, as follows.
Motor-driven metering pump working principle
The motor drives the worm gear through the coupling and makes the spindle and eccentric wheel to make rotary motion by decelerating the worm gear, and the eccentric wheel drives the sliding adjustment seat of the bow-type connecting rod to make reciprocating motion. When the plunger moves to the back dead center, a vacuum is gradually formed in the pump cavity and the suction valve is opened to suck in the liquid; when the plunger moves to the front dead center, the suction valve is closed and the discharge valve is opened and the liquid is discharged when the plunger moves further. In the pump’s reciprocal cycle of work to form a continuous pressure, quantitative discharge of liquid.
Solenoid-driven metering pump working principle
The electromagnetic actuator drives the diaphragm in the pump head reciprocating motion, causing changes in the volume and pressure of the pump head chamber, the change in pressure causes the opening or closing of the suction and discharge valves to achieve quantitative liquid intake and discharge. Please see the principle of solenoid dosing pump for details.
Type of dosing pumps
Solenoid dosing pumps – use electromagnetism as the driving force. When the solenoid is energized, it attracts the plunger on the solenoid. It then creates a reciprocating motion to move the diaphragm to draw in the right amount of fluid.

Diaphragm metering pump – built-in diaphragm, can convey all kinds of corrosive liquids, widely used.

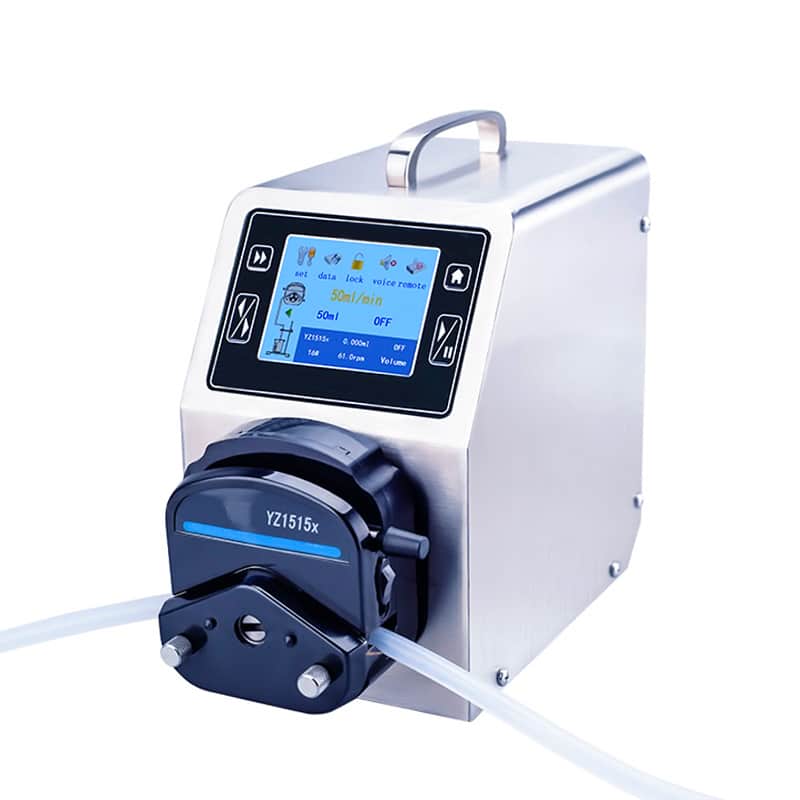
Peristaltic dosing pumps – A section of pump tubing between two rotating rollers to form a “pillow” of fluid. Accurate metering but low flow rate.

Plunger pump – rely on the plunger in the cylinder reciprocating movement, so that the volume of the sealed working chamber changes to achieve oil suction, oil pressure. Widely used in high-pressure, high-flow applications.

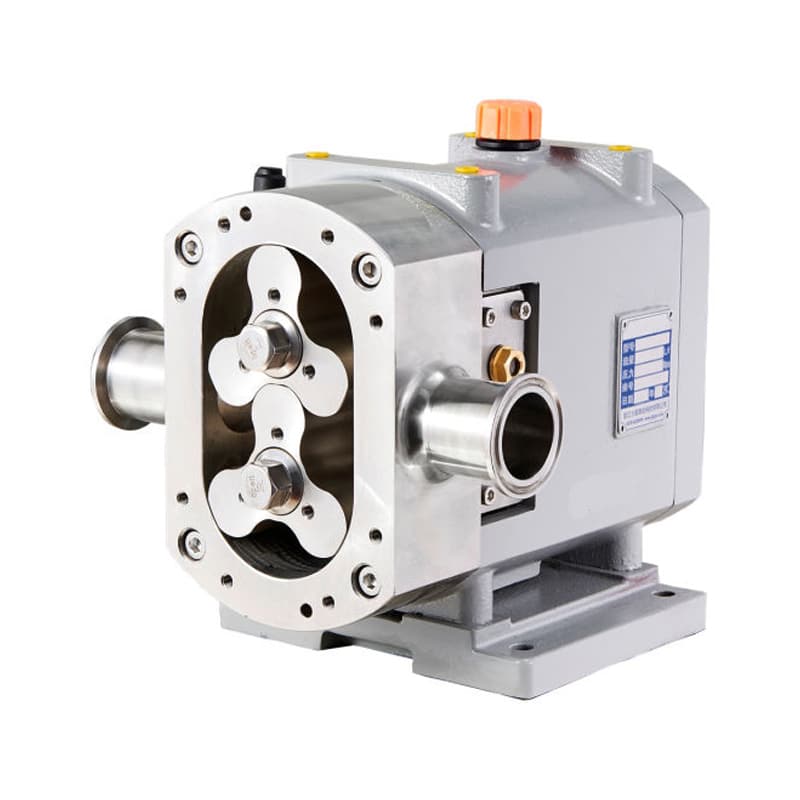
Lobe pumps – with two rotors in synchronous motion, constituting a higher vacuum and discharge pressure, especially suitable for the transfer of pharmaceutical grade media and corrosive high viscosity media.

Metering pump applications
Metering pumps are widely used in petroleum, chemical, oil refining, electric power, food, environmental protection, mining, water treatment, textile, paper, medicine and so on. Among them, water treatment industry is the most widely used, such as:
- Industrial water treatment: cooling towers and boiler circulating water treatment to add scale inhibitor, anticorrosion agent
- Industrial wastewater treatment: flocculation, oxidant, defoaming, pH adjustment
- Power plant water treatment: boiler water treatment
Chemical dosing system
As the core part of the chemical dosing system, the dosing pump undertakes the dosing metering function. The main components of the dosing system are as follows.
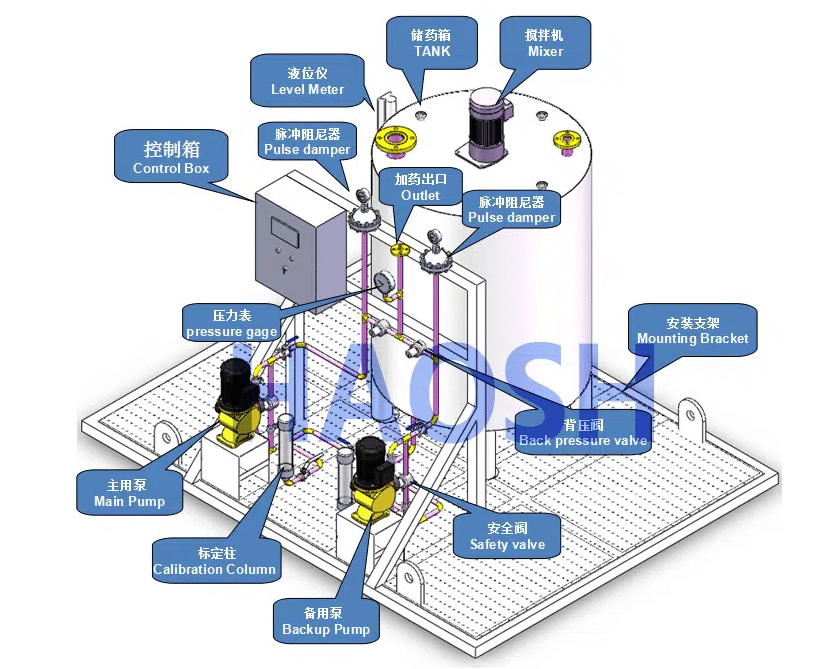
- Chemical storage tank — holds the product to be dosed
- Dosing pump — varies in material and size, includes inlet, suction line, and dosing line
- Injector — a one-way valve that injects the chemical into the product
- Foot valve — check valve connected to the suction line
- Dosing line — hose, can be PE, PVC or stainless steel for high pressure applications
- Control system — ensures accuracy, opens and closes at specific times. Can be a simple flow switch or timer
- Flow meter — float flow meter or electromagnetic flow meter to measure real-time liquid flow in the pipeline
- Mixer agitator – Used to mix even chemicals to help prepare desired solutions
What is API 675 standard?
API 675 is a comprehensive standard published by the American Petroleum Institute (API) that defines the requirements for reciprocating metering pumps used in service in the petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries. It is typically applied to hydraulic diaphragm pumps or piston pumps.



